Creating new layers
(→= Creating database tables for the topic map) |
(→Creating database tables for the topic map) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
Database connection can be established to an existing or a new database. If you are configuring fresh database you probably want to create tables for the database. Database creation files locate in '''conf/database''' folder. There is separate files database creation files to '''MySQL''', '''Microsoft SQL Server''', '''HSQL''' and generic SQL database. Detailed database initialization steps are beyond the scope of this chapter but in MySQL the steps are | Database connection can be established to an existing or a new database. If you are configuring fresh database you probably want to create tables for the database. Database creation files locate in '''conf/database''' folder. There is separate files database creation files to '''MySQL''', '''Microsoft SQL Server''', '''HSQL''' and generic SQL database. Detailed database initialization steps are beyond the scope of this chapter but in MySQL the steps are | ||
| − | + | Log in the MySQL server with | |
mysql --user=<user_name> --password=<password> | mysql --user=<user_name> --password=<password> | ||
| − | + | Create empty database for the topic map layer | |
create database mytopicmap; | create database mytopicmap; | ||
| − | + | Import database creation clauses from '''db_mysql.sql''' | |
source db_mysql.sql | source db_mysql.sql | ||
| − | + | Set database user name and password | |
grant all on mytopicmap.* to "username"@"%" identified by "password"; | grant all on mytopicmap.* to "username"@"%" identified by "password"; | ||
Revision as of 20:12, 20 October 2006
Topic map standard defines a merge operation between identical topics. Merge operation is extremely powerful as it allows incremental knowledge building. Knowledge packets addressing same topics superposition. The only problem with merge rules is that the source of topic changes is lost. You can't recognise which source assigned which topic element. Backtracking the merge changes is essential to ensure trust between knowledge sources and knowledge aggregator.
Wandora supports layered topic maps. Layered topic map contains one or more topic maps stacked into an ordered array. Wandora allows you to add and delete topic maps in the layer stack. You can also make topic map layer invisible and lock layer if you decide not to change layer's contents.
Wandora's layer stack locates in bottom left corner. When you start Wandora, application reads topic map from conf/wandora.xtm and creates the layer Base for it.
To create another layer you can
- Drag and drop XTM, LTM or RDF(S) file to the layer stack. Wandora imports the file and creates a new memory layer for the imported file.
- Select Layers > New layer or press ALT+N. This opens layer creating window used to define layer type and properties. Current version of Wandora supports memory, database and remote layers. Layer type defines also the source of topic map.
Contents |
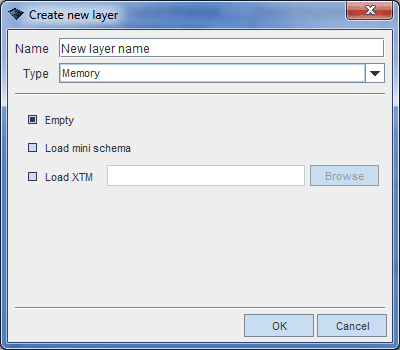
Creating Memory Layer
Configuring new memory layer is very easy. You can only import XTM topic map file to the layer. Below is an example of memory layer configuration panel.
Creating empty topic map does not actually create empty topic map but imports conf/wandora_mini.xtm to the created layer. This mini map contains a set of Wandora's fundamental topics and associations. In order to get absolutely empty topic map use Layer > Clear layer topic map... tool.
Creating Database Layer
To create a database layer is more complicated. If you have configured the layer during previous Wandora sessions, you can simply pick up the layer configuration. Below is an example of database layer selection window.
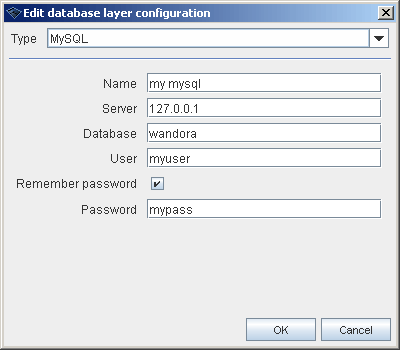
If you have not configured the layer before you need to create a configuration for the layer. Conguration is created clicking New button in database layer selection window. This opens configuration window shown below
To define database configuration you have to select database type first. Current version of Wandora supports two specific and one generic database types. Specific types are for MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server. Generic database type allows you to create database layer with any JDBC capable SQL database.
Setting up MySQL or Microsoft SQL Server database configuration you need to enter
- Database configuration name.
- IP or domain name for the database server.
- Database's name.
- Name of valid database user.
- Password for the database user. Although Wandora suggests that you can enter database password later without remembering it, current Wandora version supports only remembered passwords. Wandora does not request password separately but layer creation fails.
Wandora's software package does not contain JDBC library for MySQL or Microsoft SQL Server. You need to download libraries separately from producer's own WWW site. See Download for specific download addresses.
Setting up generic database configuration you need to enter
- Database configuration name.
- Database JDBC driver class name.
- Connection string.
- Database user.
- Database user password.
- SQL clauses used to initialize the database.
Creating database tables for the topic map
Database connection can be established to an existing or a new database. If you are configuring fresh database you probably want to create tables for the database. Database creation files locate in conf/database folder. There is separate files database creation files to MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, HSQL and generic SQL database. Detailed database initialization steps are beyond the scope of this chapter but in MySQL the steps are
Log in the MySQL server with
mysql --user=<user_name> --password=<password>
Create empty database for the topic map layer
create database mytopicmap;
Import database creation clauses from db_mysql.sql
source db_mysql.sql
Set database user name and password
grant all on mytopicmap.* to "username"@"%" identified by "password";
And the database is ready to be used as a layer in Wandora.