Creating new layers
(→Restoring database topic map) |
(→See also) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Topic map standard defines a merge operation between identical topics. Merge operation is extremely powerful as it allows incremental knowledge building. Knowledge packets addressing same topics superposition. The only problem with merge rules is that the source of topic is lost. You can't recognize which source assigned which topic element. Backtracking the merge | + | Topic map standard defines a merge operation between identical topics. Merge operation is extremely powerful as it allows incremental knowledge building. Knowledge packets addressing same topics superposition. The only problem with merge rules is that the source of topic is lost. You can't recognize which source assigned which topic element. Backtracking the merge is essential because original topics may contain errors. Backtracking also ensures trust between knowledge sources and aggregators. One backtracking method is to allow the aggregator to cancel and redo the merge easily. |
Wandora supports layered topic maps. Layered topic map contains one or more topic maps stacked into an ordered array. Wandora user can add and delete topic maps in the layer stack. User can also make topic map layer invisible and lock layers. | Wandora supports layered topic maps. Layered topic map contains one or more topic maps stacked into an ordered array. Wandora user can add and delete topic maps in the layer stack. User can also make topic map layer invisible and lock layers. | ||
| − | The concept of layers and layer stack in Wandora is similar to the layer concept of many graphic creation and manipulation applications such as Adobe's PhotoShop where single image may contain multiple layers and graphics designer manipulates one layer at time. Layer implementation in graphic application ables the designer to isolate finished image parts from unfinished and enables rapid versioning. This is the motivation behind Wandora's layer implementation also. To make designer's life easier. | + | The concept of layers and layer stack in Wandora is similar to the layer concept of many graphic creation and manipulation applications such as Adobe's PhotoShop where single image may contain multiple layers and graphics designer manipulates one layer at a time. Layer implementation in graphic application ables the designer to isolate finished image parts from unfinished and enables rapid versioning. This is the motivation behind Wandora's layer implementation also. To make designer's life easier. |
| − | Wandora's layer stack locates in bottom left corner of Wandora window. When you start Wandora, application reads topic map from '''conf/wandora.xtm''' and creates the layer '''Base''' for it. | + | Wandora's layer stack locates in bottom left corner of Wandora window. When you start Wandora, application reads topic map from '''conf/wandora.xtm''' and creates the layer '''Base''' for it. Next image views a layer stack with three layers. Layer '''Base''' is active. |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:layer_stack_and_three_layers.gif|center]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | To create another layer you can | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | To create | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * Drag and drop XTM, LTM, JTM, RDF(S) or OBO file to the layer stack. Wandora imports the file and creates a new memory layer for the imported file. | |
| + | * Select '''Layers > [[NewLayer|New layer]]''' or press '''ALT+N'''. This opens a layer creating dialog used to define layer type and properties. | ||
| − | + | Wandora supports multiple different data storage options for topic maps. Usually memory stored topic map, i.e. Memory topic map is sufficient. However, the amount of memory limits also the size of potential topic maps. Database storage option is available for large topic maps with millions of topics and associations. Wandora also introduces special topic map constructs used to stack multiple topic maps into a single topic map, to filter and to mirror existing topic maps. Current version of Wandora supports next layer types: | |
| + | * [[Layered topic map]]s | ||
| + | * [[Memory topic map]]s | ||
| + | * [[Database topic map]]s | ||
| + | * [[Query topic map]]s | ||
| + | * [[Linked topic map]]s | ||
| + | * [[Remote topic map]]s | ||
| − | + | Next image views a Create new layer dialog window used to create memory layer. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:new_layer_memory.gif|center]] | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == See also == |
| − | + | * [[Introduction to Layered Topic Maps]] | |
| + | * [[Layer order and arranging layers]] | ||
| + | * [[Topic's layer distribution]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:45, 3 December 2013
Topic map standard defines a merge operation between identical topics. Merge operation is extremely powerful as it allows incremental knowledge building. Knowledge packets addressing same topics superposition. The only problem with merge rules is that the source of topic is lost. You can't recognize which source assigned which topic element. Backtracking the merge is essential because original topics may contain errors. Backtracking also ensures trust between knowledge sources and aggregators. One backtracking method is to allow the aggregator to cancel and redo the merge easily.
Wandora supports layered topic maps. Layered topic map contains one or more topic maps stacked into an ordered array. Wandora user can add and delete topic maps in the layer stack. User can also make topic map layer invisible and lock layers.
The concept of layers and layer stack in Wandora is similar to the layer concept of many graphic creation and manipulation applications such as Adobe's PhotoShop where single image may contain multiple layers and graphics designer manipulates one layer at a time. Layer implementation in graphic application ables the designer to isolate finished image parts from unfinished and enables rapid versioning. This is the motivation behind Wandora's layer implementation also. To make designer's life easier.
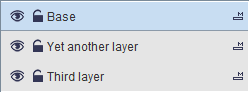
Wandora's layer stack locates in bottom left corner of Wandora window. When you start Wandora, application reads topic map from conf/wandora.xtm and creates the layer Base for it. Next image views a layer stack with three layers. Layer Base is active.
To create another layer you can
- Drag and drop XTM, LTM, JTM, RDF(S) or OBO file to the layer stack. Wandora imports the file and creates a new memory layer for the imported file.
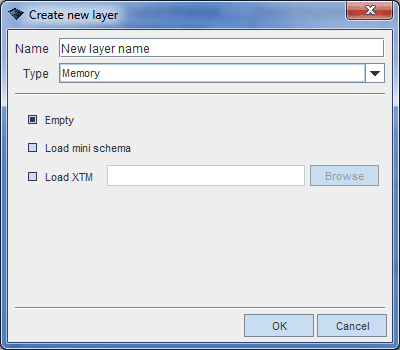
- Select Layers > New layer or press ALT+N. This opens a layer creating dialog used to define layer type and properties.
Wandora supports multiple different data storage options for topic maps. Usually memory stored topic map, i.e. Memory topic map is sufficient. However, the amount of memory limits also the size of potential topic maps. Database storage option is available for large topic maps with millions of topics and associations. Wandora also introduces special topic map constructs used to stack multiple topic maps into a single topic map, to filter and to mirror existing topic maps. Current version of Wandora supports next layer types:
- Layered topic maps
- Memory topic maps
- Database topic maps
- Query topic maps
- Linked topic maps
- Remote topic maps
Next image views a Create new layer dialog window used to create memory layer.